You could win one of two €100 One4All vouchers. (5–10 minutes)

Take our short Customer Satisfaction Survey and tell us how we can improve. You could win one of two €100 One4All vouchers. (5–10 minutes)
06 October 2022, 11am. Results from this publication ‘Output, Input and Income in Agriculture – Final Estimate 2021’ are revised. Shortly after publication in June 2022 and prior to compiling the Regional Accounts for Agriculture 2021, revised data on forage plants and compensation of employees for the years 2017 to 2021 were received. Given the number of years impacted by the revisions and the timing of their receipt, a decision was made to incorporate the revisions into the Regional Accounts for Agriculture 2021 publication and to revise this release to ensure that the State totals in both publications are aligned. As a result of the revisions to the estimated values of forage plants and compensation of employees, the value of crops, goods output at producer prices, agricultural output at basic prices, intermediate consumption, operating surplus and entrepreneurial income also changed.
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | ||
| € million | Annual Change (%) | |||||
| Goods output1 | 7,955 | 8,366 | 9,605 | 5.2 | 14.8 | |
| Intermediate consumption1 | 5,597 | 5,615 | 6,126 | 0.3 | 9.1 | |
| Net subsidies | 1,736 | 1,757 | 1,727 | 1.2 | -1.7 | |
| Operating surplus1 | 2,863 | 3,146 | 3,700 | 9.9 | 17.6 | |
| 1 Revised: 06/10/2022 | ||||||
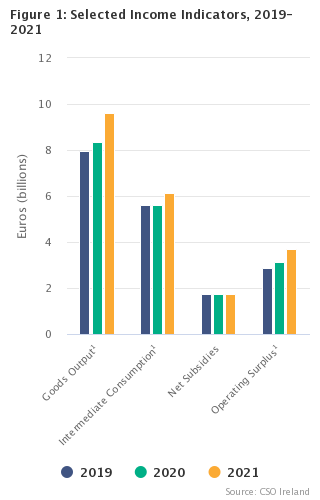
After incorporating the necessary revisions to previous years’ data arising mainly from the receipt of data from the 2020 Census of Agriculture, the CSO’s final estimate of agricultural operating surplus for 2021 shows an annual increase of €553.2m1 (+17.6%1), up from €3,146.4m1 in 2020 to €3,699.6m1. The value of agricultural output at basic prices rose by €1,214.5m1 (+13.7%1), with milk accounting for over half of this growth (€641.8m). Intermediate consumption costs rose by €510.7m1 (+9.1%1) to €6,125.8m1. See Table 1.
An analysis of the results for 2021 compared to 2020 identified the following main changes:
A 1.9% expansion in production volumes helped to moderate the impact of lower prices (-9.4%), resulting in the value of pig production decreasing by €46.5m (-7.7%) from €601.9m to €555.4m.
While the volume of sheep production declined by 1.3%, strong price growth (+21.1%) resulted in the value of sheep output increasing by €59.7m (+19.7%), from €303.3m in 2020 to €362.9m in 2021.
Milk prices continued to rise in 2021, growing by 17.0%, and with output expanding by 5.5%, the value of milk production grew by €641.8m (+23.3%), from €2,753.6m to €3,395.4m.
While the area planted with cereals was only marginally higher (+3.4%), favourable weather conditions contributed to significantly improved yields for cereals. When combined with stronger prices, the value of cereal production grew by €144.7m (+50.0%) to €434.2m in 2021. Potato yields were also significantly up and with output growing by 41.1% and prices also rising, the overall value of potatoes rose by €56.6m to €174.9m. In total, the volume of crop production increased by 9.1% and with stronger prices (+2.0%1), the value of crops rose by €209.3m1 (+10.9%1) to €2,136.3m1.
Intermediate consumption costs rose by €510.7m1 (+9.1%1), from €5,615.1m1 to €6,125.8m1.
The volume of feedingstuffs consumed on Irish farms increased by 6.8%. The impact of increased volumes was exacerbated by higher prices (+10.3%), resulting in the overall cost of feedingstuffs rising by €273.2m (+17.9%) to €1,798.4m.
The cost of fertilisers grew by €73.2m (+13.7%) to €605.5m. It should be noted that due to the methodology used to value fertilisers, the full impact of the large increase in fertiliser prices in 2021 will not be felt until estimates for 2022 are prepared.
The cost of energy and lubricants rose by €78.7m (+20.9%) due to a combination of a 15.2% increase in prices and a 5.0% rise in the volumes consumed.
Expenditure on maintenance and repairs increased by €23.1m (+4.4%) to €545.6m while expenditure on other goods and services grew by €36.6m (+7.2%) to €546.0m.
1 Values updated 6/10/2022 to reflect the changes arising from revisions to the value of Forage Plants and Compensation of Employees.
|
The recent 2020 Census of Agriculture (CoA) results identified a need for a revision of some historic agriculture data going back to 2017. The data directly impacted was the number of people in paid employment and the area of land rented. The CoA also showed changes to the number of farms by farm type and size class, data that is used to estimate many intermediate consumption costs. In addition, Brexit and the rules governing trade outside of the EU led to the identification of misclassified trade data that impacted on our estimates of poultry. As a result of these various issues, we have revised our estimates of Output, Input and Income in Agriculture for the years 2017 onwards. |
| Table 1: Output, Input and Income in Agriculture, 2019–2021 | €m | ||
| Description | Estimated Value (at current prices) | ||
| 20191 | 20201 | 2021 | |
| Livestock (incl. stock changes) | 3,380.0 | 3,606.8 | 3,989.0 |
| Cattle | 2,143.9 | 2,290.5 | 2,580.7 |
| Pigs | 543.0 | 601.9 | 555.4 |
| Sheep | 260.8 | 303.3 | 362.9 |
| Horses | 255.5 | 224.2 | 301.9 |
| Poultry | 176.8 | 187.0 | 188.1 |
| Livestock products | 2,689.7 | 2,832.6 | 3,479.9 |
| Milk | 2,608.6 | 2,753.6 | 3,395.4 |
| Other livestock products | 81.1 | 79.0 | 84.5 |
| Crops (incl. stock changes)3 | 1,885.0 | 1,927.0 | 2,136.3 |
| Barley | 218.7 | 215.9 | 282.9 |
| Wheat | 77.4 | 45.6 | 108.4 |
| Oats | 31.1 | 28.1 | 42.9 |
| Potatoes | 156.3 | 118.3 | 174.9 |
| Mushrooms | 119.2 | 123.8 | 127.7 |
| Other fresh vegetables | 108.1 | 115.5 | 120.3 |
| Fresh fruit | 55.1 | 56.1 | 57.6 |
| Other crops | 82.3 | 96.7 | 105.0 |
| Forage plants3 | 1,036.8 | 1,127.1 | 1,116.6 |
| Goods output at producer prices3 | 7,954.7 | 8,366.4 | 9,605.2 |
| Contract work | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 |
| Subsidies on products | 150.6 | 147.2 | 90.1 |
| Taxes on products | 51.1 | 52.6 | 52.9 |
| Agricultural output at basic prices3 | 8,498.2 | 8,891.8 | 10,106.3 |
| Intermediate consumption3 | 5,597.1 | 5,615.1 | 6,125.8 |
| Feedingstuffs | 1,489.9 | 1,525.2 | 1,798.4 |
| Fertilisers | 578.3 | 532.3 | 605.5 |
| FISIM2 | 134.6 | 114.5 | 77.3 |
| Seeds | 78.5 | 74.5 | 74.1 |
| Energy and lubricants | 429.1 | 377.0 | 455.7 |
| Maintenance and repairs | 477.2 | 522.5 | 545.6 |
| Other goods and services | 547.4 | 509.4 | 546.0 |
| Crop protection products | 82.8 | 79.1 | 99.4 |
| Veterinary expenses | 303.8 | 325.4 | 347.7 |
| Forage plants3 | 1,031.7 | 1,124.3 | 1,112.2 |
| Contract work | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 |
| Gross value added at basic prices | 2,901.1 | 3,276.7 | 3,980.5 |
| Fixed capital consumption | 972.9 | 993.7 | 1,094.8 |
| Machinery, equipment, etc. | 491.1 | 504.5 | 551.3 |
| Farm buildings | 481.9 | 489.2 | 543.4 |
| Net value added at basic prices | 1,928.2 | 2,283.1 | 2,885.8 |
| Other subsidies less taxes on production | 1,636.1 | 1,662.6 | 1,690.1 |
| Factor income | 3,564.3 | 3,945.7 | 4,575.8 |
| Compensation of employees3 | 701.7 | 799.3 | 876.3 |
| Operating surplus3 | 2,862.6 | 3,146.4 | 3,699.6 |
| Interest less FISIM | 18.3 | 34.0 | 64.5 |
| Land rental | 385.6 | 470.0 | 547.5 |
| Entrepreneurial income3 | 2,458.7 | 2,642.4 | 3,087.6 |
| 1 Revised: 30/06/2022 | |||
| 2 FISIM: Financial Intermediation Services Indirectly Measured. (See Background Notes). | |||
| 3 Revised: 06/10/2022 | |||
| Table 2: Selected Volume Indices, 2019–2021 | |||
| Base year: 2015=100 | |||
| Description | 20191 | 20201 | 2021 |
| Goods output at producer prices | 110.6 | 112.7 | 117.2 |
| Livestock2 | 105.5 | 108.3 | 108.9 |
| Cattle | 103.5 | 104.9 | 104.3 |
| Pigs | 104.6 | 111.8 | 113.9 |
| Sheep | 108.6 | 113.9 | 112.4 |
| Horses | 106.8 | 102.8 | 114.8 |
| Poultry | 133.7 | 153.0 | 153.2 |
| Livestock products | 124.9 | 129.6 | 136.6 |
| Milk | 124.9 | 129.8 | 136.9 |
| Crops2 | 104.7 | 102.4 | 111.8 |
| Barley | 120.3 | 113.3 | 123.9 |
| Wheat | 118.6 | 60.9 | 125.3 |
| Potatoes | 99.2 | 81.0 | 114.3 |
| Fresh vegetables | 98.7 | 102.2 | 103.1 |
| Intermediate consumption | 108.2 | 109.6 | 114.8 |
| Feedingstuffs | 115.1 | 119.7 | 127.8 |
| Fertilisers | 112.8 | 114.9 | 122.2 |
| Seeds | 118.4 | 131.1 | 124.2 |
| Energy and lubricants | 101.6 | 97.0 | 101.8 |
| Maintenance and repairs | 106.4 | 115.4 | 118.1 |
| Other goods and services | 108.5 | 100.3 | 107.0 |
| Crop protection products | 106.5 | 101.6 | 126.5 |
| Veterinary expenses | 105.1 | 111.0 | 117.2 |
| Gross value added at basic prices | 122.5 | 124.4 | 124.7 |
| 1 Revised: 30/06/2022 | |||
| 2 Including changes in stocks | |||
| Table 1A: Revisions to Output, Input and Income in Agriculture - Final Estimate 2019-2021 | €m | ||||||||||
| Description | Published Estimated Value (at current prices) | Revised Estimated Value (at current prices) | Difference Between Published and Revised Estimates (at current prices) | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||
| Livestock (incl. stock changes) | 3,380.0 | 3,606.8 | 3,989.0 | 3,380.0 | 3,606.8 | 3,989.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Cattle | 2,143.9 | 2,290.5 | 2,580.7 | 2,143.9 | 2,290.5 | 2,580.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Pigs | 543.0 | 601.9 | 555.4 | 543.0 | 601.9 | 555.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Sheep | 260.8 | 303.3 | 362.9 | 260.8 | 303.3 | 362.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Horses | 255.5 | 224.2 | 301.9 | 255.5 | 224.2 | 301.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Poultry | 176.8 | 187.0 | 188.1 | 176.8 | 187.0 | 188.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Livestock products | 2,689.7 | 2,832.6 | 3,479.9 | 2,689.7 | 2,832.6 | 3,479.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Milk | 2,608.6 | 2,753.6 | 3,395.4 | 2,608.6 | 2,753.6 | 3,395.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Other livestock products | 81.1 | 79.0 | 84.5 | 81.1 | 79.0 | 84.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Crops (incl. stock changes) | 1,979.7 | 2,006.3 | 2,241.3 | 1,885.0 | 1,927.0 | 2,136.3 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Barley | 218.7 | 215.9 | 282.9 | 218.7 | 215.9 | 282.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Wheat | 77.4 | 45.6 | 108.4 | 77.4 | 45.6 | 108.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Oats | 31.1 | 28.1 | 42.9 | 31.1 | 28.1 | 42.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Potatoes | 156.3 | 118.3 | 174.9 | 156.3 | 118.3 | 174.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Mushrooms | 119.2 | 123.8 | 127.7 | 119.2 | 123.8 | 127.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Other fresh vegetables | 108.1 | 115.5 | 120.3 | 108.1 | 115.5 | 120.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Fresh fruit | 55.1 | 56.1 | 57.6 | 55.1 | 56.1 | 57.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Other crops | 82.3 | 96.7 | 105.0 | 82.3 | 96.7 | 105.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Forage plants | 1,131.5 | 1,206.4 | 1,221.6 | 1,036.8 | 1,127.1 | 1,116.6 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Goods output at producer prices | 8,049.4 | 8,445.8 | 9,710.2 | 7,954.7 | 8,366.4 | 9,605.2 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Contract work | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Subsidies on products | 150.6 | 147.2 | 90.1 | 150.6 | 147.2 | 90.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Taxes on products | 51.1 | 52.6 | 52.9 | 51.1 | 52.6 | 52.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Agricultural output at basic prices | 8,592.9 | 8,971.1 | 10,211.3 | 8,498.2 | 8,891.8 | 10,106.3 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Intermediate consumption | 5,691.8 | 5,694.4 | 6,230.8 | 5,597.1 | 5,615.1 | 6,125.8 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Feedingstuffs | 1,489.9 | 1,525.2 | 1,798.4 | 1,489.9 | 1,525.2 | 1,798.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Fertilisers | 578.3 | 532.3 | 605.5 | 578.3 | 532.3 | 605.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| FISIM | 134.6 | 114.5 | 77.3 | 134.6 | 114.5 | 77.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Seeds | 78.5 | 74.5 | 74.1 | 78.5 | 74.5 | 74.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Energy and lubricants | 429.1 | 377.0 | 455.7 | 429.1 | 377.0 | 455.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Maintenance and repairs | 477.2 | 522.5 | 545.6 | 477.2 | 522.5 | 545.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Other goods and services | 547.4 | 509.4 | 546.0 | 547.4 | 509.4 | 546.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Crop protection products | 82.8 | 79.1 | 99.4 | 82.8 | 79.1 | 99.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Veterinary expenses | 303.8 | 325.4 | 347.7 | 303.8 | 325.4 | 347.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Forage plants | 1,126.3 | 1,203.6 | 1,217.2 | 1,031.7 | 1,124.3 | 1,112.2 | -94.7 | -79.3 | -105.0 | ||
| Contract work | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 | 444.0 | 430.8 | 464.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Gross value added at basic prices | 2,901.1 | 3,276.7 | 3,980.5 | 2,901.1 | 3,276.7 | 3,980.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Fixed capital consumption | 972.9 | 993.7 | 1,094.8 | 972.9 | 993.7 | 1,094.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Machinery, equipment, etc. | 491.1 | 504.5 | 551.3 | 491.1 | 504.5 | 551.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Farm buildings | 481.9 | 489.2 | 543.4 | 481.9 | 489.2 | 543.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Net value added at basic prices | 1,928.2 | 2,283.1 | 2,885.8 | 1,928.2 | 2,283.1 | 2,885.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Other subsidies less taxes on production | 1,636.1 | 1,662.6 | 1,690.1 | 1,636.1 | 1,662.6 | 1,690.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Factor income | 3,564.3 | 3,945.7 | 4,575.8 | 3,564.3 | 3,945.7 | 4,575.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Compensation of employees | 819.7 | 992.0 | 1,088.6 | 701.7 | 799.3 | 876.3 | -118.0 | -192.8 | -212.4 | ||
| Operating surplus | 2,744.6 | 2,953.7 | 3,487.2 | 2,862.6 | 3,146.4 | 3,699.6 | 118.0 | 192.8 | 212.4 | ||
| Interest less FISIM | 18.3 | 34.0 | 64.5 | 18.3 | 34.0 | 64.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Land rental | 385.6 | 470.0 | 547.5 | 385.6 | 470.0 | 547.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Entrepreneurial income | 2,340.8 | 2,449.6 | 2,875.3 | 2,458.7 | 2,642.4 | 3,087.6 | 118.0 | 192.8 | 212.4 | ||
Three sets of estimates are prepared in each 12-month period. The first or Advance estimate is generally released in early December of the reference year. This is based on the data available at the time, which is not fully complete. The Advance estimate is updated in March of the following year when the Preliminary estimate is published. This incorporates all additional up-to-date information that has become available by that time. In June, the Final estimate of the agricultural accounts is prepared based on the complete set of data. The methodology used for producing accounts for agriculture is based on the European System of Accounts (ESA 2010). For details of methodology and description of data sources please refer to the release's Methodology page.
This is the price received by the farmer for agricultural produce. It is sometimes referred to as the farm-gate or ex-farm price. It excludes VAT.
The basic price corresponds to the producer price plus any subsidies directly linked to a product minus any taxes on products. VAT is excluded.
This is the total output of goods produced and sold by the agricultural sector during the year valued at producer prices. It does not include the value of services provided, i.e. contract work.
Activities performed by agricultural contractors directly linked to the production of agricultural products (for example harvesting) are an integral part of agriculture. The value of such work is included both as an output and as intermediate consumption. Estimates of the input costs incurred by agricultural contractors in the provision of agricultural services are included under the appropriate intermediate consumption categories, as well as in the compensation of employees’ figure.
Subsidies and taxes on agricultural products are those paid or levied per unit of a good or service produced or exported. An example of subsidies on product is the Beef Data & Genomics Programme (BDGP). The Bovine Tuberculosis (TB) Eradication Scheme levy is an example of a tax on products.
This is the sum of goods output at producer prices plus the value of services provided (contract work) plus subsidies less taxes on products.
This is the value of all goods and services used as inputs in the production process excluding fixed assets (capital goods), whose consumption is recorded as fixed capital consumption (depreciation). Intermediate consumption excludes the cost of acquiring new or existing fixed assets, e.g. tractors, agricultural machinery etc. They are recorded as gross fixed capital formation (GFCF). Intermediate consumption includes expenditure on contract work and forage plants, even if consumed within the same agricultural holding.
The production of forage plants is valued as part of output. Silage and hay are the main items in this category. Direct sales of cereals between farms and use of cereals within farms are also included under forage plants. These items are also treated as intermediate consumption with minor exceptions, such as sales of straw to racing stables.
Financial intermediaries (mainly banks) charge explicit commissions and fees for their services to customers, as well as implicit ones by paying and charging different rates of interest to borrowers and lenders. The revenue from the margin on lending and borrowing by financial intermediaries is described as Financial Intermediation Services Indirectly Measured (FISIM). The inclusion of FISIM in the table is in line with recommended EU national accounting conventions. It is a reallocation to intermediate consumption of part of the interest paid by farmers. While the inclusion of FISIM will increase intermediate consumption and decrease gross value added, it will decrease, by the same amount, the figure shown for interest paid.
This is the difference between the output at basic prices and intermediate consumption. It is a measure of gross income before depreciation, subsidies and taxes on production and compensation of employees.
This relates to the foreseeable wear and tear and obsolescence of fixed capital goods. It is calculated on the basis of the probable economic life of the asset. It is not calculated for breeding livestock or for non-produced assets such as land.
Net value added is calculated by subtracting expenditure on fixed capital consumption (depreciation) from gross value added.
Other subsidies on production are subsidies other than those on products. Examples are the Basic Payment Scheme, the Areas of Natural Constraints scheme and GLAS. Subsidies on production also include any VAT over compensation that may arise under the flat rate farmers’ scheme. Taxes on production consist of motor and machinery tax paid by farmers. If the operation of the farmers’ flat rate scheme results in an under compensation of VAT, this is also included as a ‘tax on production’. Other subsidies less taxes on production are not included in the calculation of output but are included in the calculation of factor income and operating surplus.
Factor income is a sum of net value added plus other subsidies on production less taxes on production. It is sometimes referred to as 'value added at factor cost'.
This includes remuneration in cash and in kind. It does not include the remuneration of work undertaken by the farm owner or by non-salaried family members.
The operating surplus is calculated by subtracting compensation of employees from factor income. The figure is comprised of the operating surplus earned by farmers and that earned by agricultural contractors. It is an estimate of income before deductions for interest payments on borrowed capital, land annuities and rent paid by farmers to landowners for the use of their land.
Entrepreneurial income is comprised of operating surplus less interest payments on borrowed capital and land rental paid by farmers to landowners.
Net subsidies is the combined value of subsidies less taxes on products plus other subsidies less taxes on production.
For each category, the difference between closing year stocks and opening year stocks is valued at the average producer price for the year.
To calculate the volume indices all items of output and input are valued at constant base year prices, i.e. by applying base year prices to current year quantities. The volume index for 2021 may then be calculated by comparing the value in 2021 at average 2015 prices to the value in 2015 at average 2015 prices. Volume indices allow one to estimate the changes in production and expenditure, as if the prices did not change since the base year. This separates the effects of volume and price changes on output, input and income.
Any revisions to previous years’ estimates are only made as part of the production process for the Final estimate release. When preparing the final estimates for the current year’s release (year T), routine revisions are made to the final estimates for the two previous years also (i.e. years T-1 and T-2). These revisions to previously published final estimates tend to be minor. For further details on the revisions policy, please refer to the release's Quality Report.
Individual figures have been rounded independently and the sum of component items therefore may not necessarily add to the totals shown.
 Hide Background Notes
Hide Background Notes
Scan the QR code below to view this release online or go to
http://www.cso.ie/en/releasesandpublications/er/oiiaf/outputinputandincomeinagriculture-finalestimate2021/